Understanding the Comprehensive Metabolic Panel Test
What is Comprehensive Metabolic Panel - CMP Test?
Did you know that you can find information about 14 different blood tests in your body using a simple and economical blood test panel called Comp Metabolic or CMP?
That's what a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) does. This panel is an expanded version of the basic metabolic panel and it checks the levels of various substances in the bloodstream, such as glucose, calcium, sodium, liver enzymes, creatinine, and others.
Why would you need to do a CMP blood test panel? Physicians order this lab test panel because they want to know more about the health of your various organs, such as the liver, pancreas, and kidneys, or whether their bodies are maintaining proper electrolyte balance.
Electrolytes are positively or negatively charged molecules (ions) that play important roles in cellular activity and heart and nerve function. Normally, electrolyte levels are regulated by the kidneys, and any excess is excreted in the urine. Most healthy people can get all the electrolytes and other minerals they need by eating a balanced diet. Electrolyte imbalances may be a sign of malnutrition, kidney issues, or dehydration (which can result from persistent vomiting or diarrhea). Such imbalances, which can affect the pH balance of the blood, are not uncommon in people with acute or chronic illnesses.
Liver function tests, also known as the hepatic panel, are laboratory tests that help measure how well the liver is working. The liver carries out many vital bodily functions; when it is not working properly, levels of various enzymes, proteins, and other substances in the blood may rise or fall. Increased liver enzyme levels may be a sign of liver damage from conditions like viral hepatitis, excessive alcohol consumption, or drug toxicity. One important enzyme that is measured in a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) test is alanine aminotransferase (ALT), which is primarily found in the liver. A CMP may also be ordered by your healthcare provider to evaluate liver and kidney function, as well as nutrient levels, to get a more complete picture of your overall health and/or to help diagnose or monitor liver disease or other specific conditions, as indicated by abnormal CMP test results.
Keep reading this article to find out more about the comprehensive metabolic panel and how it can benefit you.
What Are the Substances Tested by the Complete Metabolic Panel?
The difference between a CMP test and a basic metabolic panel is that the comprehensive one includes liver tests as well. Here are the 14 substances tested by the CMP lab:
1. Sodium
Sodium is a vital electrolyte in the bloodstream and is useful for a wide variety of bodily functions. You get sodium in your body by eating salty food products. Sodium is usually excreted through sweating. This substance needs to be present in adequate amounts in the bloodstream. Otherwise, health issues might occur.
For example, too much sodium in the body can make the blood more acidic. As a result, a wide variety of health conditions can appear, such as heart problems, digestive issues, etc. Too little sodium in the body can lead to lethargy and confusion, especially in seniors. Sodium retention can cause edema and bloating.
2. Potassium
Potassium is another vital electrolyte in the human body. It helps to regulate muscle contractions and maintain a healthy nervous system. Similar to sodium, potassium can also be eliminated through sweating.
You can get more potassium in your body by eating beans, bananas, and spinach. If you don't have enough potassium in the bloodstream, then different symptoms can occur, such as muscle aches, fatigue, confusion, mood changes, and even breathing difficulties.
When kidneys fail, they cannot remove excess potassium from the body. This allows the extra potassium to build up and cause problems. Having high levels of potassium in the blood is called hyperkalemia, which is common in people with advanced CKD. High-potassium levels usually develop gradually. Too much potassium in your blood can lead to dangerous, and possibly deadly, changes in heart rhythm.
3. Chloride
This electrolyte is also essential in the human body because it maintains adequate levels of fluids inside and outside of cells. It performs other functions such as keeping the blood pressure in normal ranges, balance pH levels, etc.
People who have a deficiency in chloride usually experience specific symptoms such as headaches and fatigue. They can also get dehydrated and lose fluids through diarrhea and vomiting. A lot of chlorides can be lost through sweating as well.
4. Carbon Dioxide
You have heard of carbon dioxide before, and you know that's an important element in respiration. Pure carbon cannot be stored or transported in the bloodstream, so the body creates carbon dioxide, which is water-soluble. This substance is necessary to inform the body when the oxygen levels are low.
When there is too little carbon dioxide in tissues and blood, this can signify certain health problems such as kidney disease, acidosis, etc. When too much carbon dioxide is present in the body, it can damage the internal organs and cause a wide variety of health complications.
5. Albumin
Albumin is one of the most essential proteins in the human body. Its main function is to regulate blood pressure. This substance binds to other hormones such as bilirubin, thyroxine, and others.
Too little albumin in the body can signify malnutrition, heart failure, or a different type of serious health problem. Symptoms include fatigue, appetite changes, and a rapid heartbeat. Too much albumin can be a sign of kidney damage or a different issue. High albumin levels might be caused by acute infections or burns.
6. Alkaline Phosphatase
This substance is responsible for breaking down proteins in the human body. It plays a vital role in the development and maintenance of bones. Having abnormal levels of alkaline phosphatase in the bloodstream can be linked to bone disorders and even liver problems. That's why it's essential to do a comprehensive metabolic panel test to verify the levels of this hormone in your body.
7. Bilirubin
The comprehensive metabolic panel also tests for bilirubin, a substance that helps to remove waste products from the system and is responsible for breaking down heme in all vertebrates. It is produced when old red blood cells are broken down and processed by the liver. Bilirubin levels in the blood can indicate how well the liver is functioning and the health of your blood vessels and immune system.
A deficiency of bilirubin can signify liver problems. People who have severe liver issues tend to develop jaundice, which is characterized by a yellowing of the eyes and skin. This happens because bilirubin is yellow and tends to float around in the bloodstream, causing jaundice and other medical problems.
Having too much bilirubin is also a bad thing because it leads to the development of gallstones. A liver that produces too much cholesterol can be the cause of too much bilirubin.
8. Aspartate Transaminase
Aspartate Transaminase is also known as Aspartate aminotransferase. This enzyme is important when it comes to the metabolism of amino acids, and it can be a good indicator of your liver's health.
Your liver is primarily responsible for producing the enzyme that the comprehensive metabolic panel tested, but other organs also produce small amounts of AST. Having too much or too little AST can signify problems with your liver, especially when this is accompanied by other symptoms such as tiredness, jaundice, dark-colored urine, bruises, etc.
9. Alanine Transaminase
The liver produces an enzyme known as alanine transaminase, which is the "brother" of aspartate transaminase. It too plays an important role in the metabolism of amino acids. In healthy individuals, the amount of ALT in the bloodstream is low. If these levels are elevated, they can indicate liver disease.
Very high levels of ALT in the bloodstream (usually ten times more than normal) can also indicate hepatitis, serious liver damage, congestive heart failure, or diabetes. People might experience high levels of ALT as a result of various underlying causes, such as muscle disease, taking certain drugs, etc.
10. Blood Urea Nitrogen
This substance is measured to determine the health of your kidneys. Your kidneys' filtering of the blood results in the waste product urea nitrogen. This substance is eliminated from the body through urine. Healthy levels of blood urea nitrogen are between 7 and 21 mg/dL.
Having higher than normal urea nitrogen levels can signify a problem with your kidneys, which needs to be investigated as soon as possible. Symptoms of having too much urea nitrogen in the bloodstream include nausea, vomiting, confusion, high blood pressure, and acidosis.
11. Total Protein
The amount of protein in your body is also important to measure. Protein is responsible with a wide variety of bodily functions and processes, including building cells, repairing muscle tissue, transporting hemoglobin, etc.
Although it's rare for people nowadays to have a protein deficiency, this can be an issue which results in muscle wasting. This process involves breaking down muscle tissue until the health of the individual is seriously deteriorates. Having too much protein in the bloodstream is also quite unusual, and it can cause indigestion, abdominal discomfort, bloating, and other similar issues.
Protein is taken from foods and beverages, and its typical ranges vary from individual to individual. Active people require more protein to repair their muscles and maintain muscle tone. Sedentary people might have smaller protein requirements. The total protein in the body indicates the overall health and wellbeing of the patient.
12. Calcium
Calcium is another important element in your body. It's responsible for numerous functions and processes, including maintaining proper bone density and teeth health. Calcium can be taken mostly from dairy products as well as certain foods such as beans, spinach, and almonds.
Having too little calcium in your bloodstream can predispose you to different bone disorders, including osteoporosis. The health of your teeth will also be affected. Having too much calcium is not a good thing, either. High levels of calcium in the bloodstream can cause kidney stones, brittle bones, and a multitude of other health complications.
13. Creatinine
Creatinine results from the breakdown of muscle tissue. The kidneys filter this substance, and urine regularly eliminates it. The amount of creatinine in the body is a good indicator of the health of your kidneys.
Many metabolic panels also include an eGFR test along with the creatinine test. eGFR stands for estimated glomerular filtration rate, and it's another test for renal function. Having too much creatinine in the bloodstream might indicate that your kidneys are not very efficient at filtering it, which can indicate a renal problem. Additionally, abnormal BMP results, including high levels of creatinine, can also indicate conditions such as kidney disease, breathing problems, and complications related to diabetes. If any of these results are abnormal, further testing may be necessary to confirm or rule out a specific diagnosis. eGFR over 60 is recommended.
14. Glucose
The last substance tested in the CMP lab is glucose, otherwise known as blood sugar.
Anything you eat or drink is converted into glucose in the bloodstream, whether it's iceberg salad or a burger. The brain primarily uses glucose for proper function, but cells also use it as an energy source.
When too much glucose is detected in the blood, the pancreas secretes insulin to open up the cells and absorb some of this glucose. When the pancreas doesn't secrete enough insulin or the cells become resistant to it, diabetes can develop. Having too much glucose in the blood regularly is not a good thing and that's why you should test its levels regularly.
Too little glucose is also detrimental to your health. Remember that glucose is used as a form of energy, so having low blood sugar levels predisposes you to rapid heartbeats, fatigue, dizziness, and confusion.
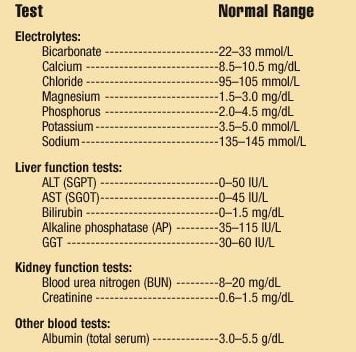
CMP Test FAQ
Now that you know what a CMP panel contains, let's find out some answers to some of the questions you might have about it.
1. How Can I Do the CMP Panel Test?
The test is done using a single blood sample. You go to a clinic and draw blood, which will be analyzed in a medical laboratory. The doctors will perform the Comprehensive Metabolic Panel Procedure, using a small needle, to take a blood sample from a vein in your arm. They'll collect the blood in test tubes or vials. You may feel a little sting or slight pain when they put the needle in or pull it out, and a small amount of blood will be collected for testing. A trained health care professional performs this quick and straightforward procedure, which typically takes less than five minutes. You get the results back in a few business days, and you can compare them against standard reference values.
2. Is the Comprehensive Metabolic Panel Test Painful?
In most cases, it's not, but it depends on whether you have a fear of needles or not. Today's doctors are very efficient at drawing blood, so you might not even feel the sting when the needle enters your vein.
3. What If Some Variables or Enzymes Are Out of Normal Ranges?
Once the results are back and you see that some substances are off the charts, you can go to your healthcare provider for recommendations. If you have high glucose levels, your doctor might recommend starting an exercise regimen, as this is known to increase insulin sensitivity and prevent diabetes.
If your calcium levels are low, you might need to eat more dairy products. If your sodium levels are high, you might want to avoid salty foods. These recommendations are based on the specific results of each, so there's no one-size-fits-all here.
4. Do I Need to Fast Before Doing the Test?
Yes, fasting is mandatory. You should avoid eating and drinking anything else but water for 12 hours before doing this test. Fasting is necessary to let the hormonal values return to baseline, so the diagnosis is more accurate.
5. Why Should I Do This Test?
It's important to do the test to get a broad overview of the hormones and enzymes in your body. If some substances are not in the comprehensive metabolic panel blood test normal ranges, you can take action and prevent more serious health complications related to a medical condition, such as maintaining proper fluid balance. Plus, the test is affordable, quick, and easy to do, making it a convenient way to check for any imbalances in your body's different substances. So why not take advantage of it?
6. How Can I Read and Interpret My Results?
The comprehensive metabolic panel normal ranges are published on the internet, and you can find them with a simple Google search. You can also ask your doctor to interpret the results for you, as well as check out this interesting CMP guide on reading your comp metabolic panel.
Ready to Take the Test?
The comp metabolic panel provides one of the best ways to take control of your health. You can order the CMP test online from DiscountedLabs.com and find out how healthy you are in just a few business days, so why not give it a try?










