How to Treat Low Carbon Dioxide in Blood: Master CO2 Blood Test Results - A Complete Guide
The CO2 blood test is important to have. It checks the CO2 levels in your body. This is vital for your health. In this guide, we will explain why CO2 levels are important. We will see how they connect to kidney and lung function.
We will explain how to take blood samples. A needle is usually put in the elbow for this test. The samples are then sent to the lab for arterial blood gas analysis. Lastly, we will talk about what normal CO2 levels are. We will also look at what can affect the test results.
As you read, you will learn about venipuncture. This is the process used to take a small amount of blood for a CO2 test. We will explain how labs analyze these samples. You will read about normal CO2 levels. We will also discuss things that can affect the test results, like certain medications.
We will explore the signs that show if your CO2 levels in the blood are too high or too low. We will also share tips on how to deal with abnormal blood test results. This includes learning the reasons behind it and creating personal treatment plans. This way, you can better understand your body and make good choices for your well-being.

What is the CO2 Blood Test?
The CO2 blood test, known as the bicarbonate test, checks the level of CO2 in your blood. It looks at how well your kidneys and lungs work. This test helps keep the acid levels balanced in your blood. It's a simple blood test often done along with an electrolyte panel or a basic metabolic panel. This test can find problems with your kidneys or lungs. Knowing about the CO2 blood test will help you take care of yourself. It will also help you read your test results better.
Why Measure Carbon Dioxide Levels
Carbon dioxide (CO2) plays a key role in how our body works. It helps control pH levels and gets rid of waste gas from cells. The kidneys and lungs help keep CO2 levels in check. They do this by removing extra CO2 through urine and by exhaling. If these processes get out of balance, it can lead to health issues like trouble breathing or problems with electrolytes. That's why it's important to check your bicarbonate level, which is a form of carbon dioxide (CO2), in your blood. This check can show how well your body is functioning.
- Kidney Function: High CO2 levels show your kidneys are not filtering waste well. This might be caused by kidney disease.
- Lung Function: Low CO2 levels indicate your lungs are not working properly. This can happen with asthma, emphysema, or COPD.
- pH Balance: Unusual CO2 levels can upset the acid-base balance in our body. This may lead to symptoms like tiredness, confusion, and trouble breathing, among others.
CO2 and Kidney and Lung Function
Understanding how our organs work together helps doctors make better treatment plans for us. For instance, if a blood gas test shows low CO2 levels, it suggests that the lungs are not working well. In this case, healthcare professionals may suggest more tests or treatments to improve lung function.
High levels of CO2 in the blood suggest that your kidneys are not doing a good job of getting rid of waste. This can lead to kidney disease. If this occurs, you will need to see a doctor.
In summary, the CO2 blood test checks the amount of CO2 in your blood. It tells you how well your kidneys and lungs are working. This test also looks at the acid balance in your body. It involves a simple blood draw. The results can give you important information about your health. It can help find breathing problems or imbalances in electrolytes, like chloride levels. If you are worried about your CO2 levels, talk to your healthcare provider. Consider asking for a CMP or an electrolyte test.
You need to know about the CO2 blood test. This test looks at the amount of CO2 in your blood. When you learn how this test works, you will understand more about yourself.
The CO2 blood test checks the level of carbon dioxide in your blood. This test shows how well your kidneys and lungs are working. When CO2 levels are not right, it can affect the acid-base balance in your body. A change in this balance can lead to health problems, like trouble breathing or issues with your electrolytes. If you are worried about your CO2 levels, talk to your healthcare provider about a carbon dioxide test. Knowing your blood test results can help you understand your lung function and overall health better.
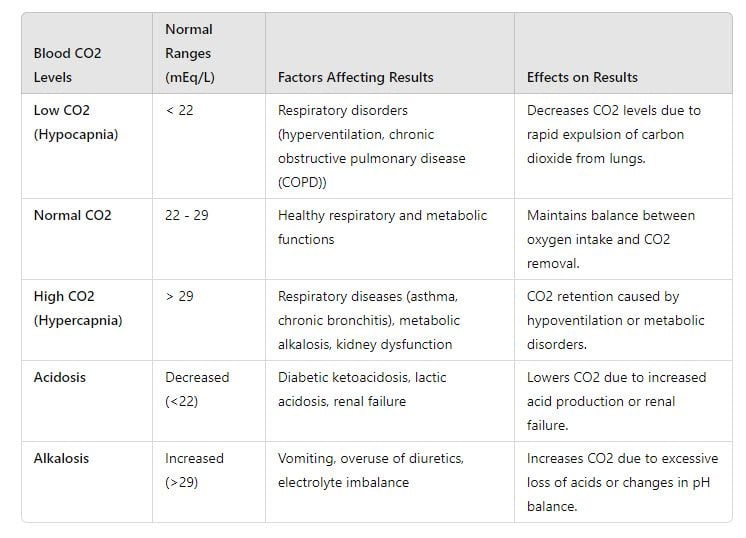
CO2 Normal Ranges and Factors that Affect Results
The CO2 blood test checks the level of carbon dioxide in your blood. This test is key to keeping the right acid balance in your body. A healthcare provider may use this test, which is also known as a carbon dioxide blood test, to find out if you have certain health conditions, diseases, or disorders. Different labs might have various normal ranges for the CO2 test. What you eat and your medications can also change your results. That's why it's very important to discuss your results with your doctor and find out the next steps.
Lab Variability in Normal Ranges
Total CO2 levels normally range from 23 to 29 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). This is about 22 to 29 millimoles per liter (mmol/L). These levels can change based on age or different lab standards. For example, the Mayo Clinic shows a range of 20 to 31 mEq/L. To better understand your test results and CO2 levels, speak with a medical professional. They can help explain the lab's reference ranges.
Medications that affect CO2 levels
Medications can change your blood test results for CO2. It is important to tell your doctor about any medications you are using before the test. Here are some examples:
- Diuretics: These make you urinate more. They can also change your electrolytes.
- Corticosteroids: These help with swelling or conditions like asthma or lupus. They can also change electrolytes.
- Blood pressure meds: Some blood pressure medications, like ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers, may affect how your kidneys work. They can change serum bicarbonate levels too.
- Antacids: Many antacid tablets, such as sodium bicarbonate or calcium carbonate, can influence CO2 levels in your blood.
Your results can change for several reasons, not just due to medications. Being dehydrated or breathing quickly can lower your CO2 levels in the blood. Kidney disease or some lung problems can make your CO2 levels go up beyond normal. Talk to your healthcare provider about your worries. This will help you understand your blood test results better.
What to Do with Test Results
If your blood test results show that CO2 levels are too high or too low, don't worry. It's important to talk to a doctor. They will help figure out what is causing the results. They will guide you on what to do next. This could mean more tests or treatment, if necessary.
In some cases, fixing health issues such as kidney problems or lung issues can help balance the acids and bases in your body. You might need further tests, like a complete metabolic panel, based on your needs. It's a good idea to talk with your health care provider for personalized advice.
Keep in mind that normal ranges can change from one lab to another. Medications can also change test results if you are having a CO2 blood test. It's also helpful to know the signs of high or low CO2 levels.
The CO2 blood test checks the amount of bicarbonate and carbon dioxide in your blood. This test is important for keeping the pH balance in your body just right. If this balance changes, it could mean you have a health issue. Normal ranges can be different from one lab to another. Your age and the medications you take can also change the results. It is a good idea to talk to a doctor to understand your results and decide what to do next if necessary.
Symptoms of High or Low CO2 Blood Levels
Abnormal CO2 levels in the blood can be connected to the lungs, kidneys, or other organs. It is important to know the signs of having too much or too little CO2. By recognizing these signs, you can find health issues early. This helps you get medical help when you really need it.
Symptoms of High CO2 in the Blood
Obesity, hypoventilation syndrome, certain medications, and lung diseases such as COPD can lead to hypercapnia. Hypercapnia is when there is too much CO2 in the blood. Here are some usual symptoms of high CO2:
- Having trouble breathing
- Feeling very tired or confused
- Getting headaches often
- Breathing quickly
- Finding it hard to focus
- Experiencing muscle shakes or cramps
If you feel any of these symptoms for a long time, you should see a doctor. A fast checkup is important. Treatment can help stop issues caused by low CO2 levels.
Low CO2 in Blood
A low CO2 level in a blood test can mean several health problems.
- Addison's disease happens when the adrenal glands do not make enough hormones. This can lead to low CO2 levels.
- Diarrhea can cause you to lose a lot of fluids and electrolytes, which may result in low CO2.
- Poisoning from things like ethylene glycol or salicylate can disturb the body's acid-base balance, leading to low CO2.
- Ketoacidosis is a serious problem for diabetics. It occurs when the body makes too many blood acids and causes low CO2.
- Kidney disease can affect how the body controls CO2 when the kidneys are not working well.
- Lactic acidosis comes from having too much lactic acid in the blood. This often happens when there is not enough oxygen, leading to low CO2.
- Respiratory alkalosis occurs when the lungs take out too much CO2, which reduces CO2 in the blood.
Respiratory acidosis happens when the lungs cannot get rid of enough CO2. This leads to a buildup of CO2 in the blood.
A low CO2 blood test result can show a health issue with the lungs, kidneys, or metabolism. More tests will be important to find out the exact reason.
Symptoms of Low CO2 in the Blood
Low carbon dioxide (CO2) in your blood can indicate an issue with the oxygen you breathe in and the CO2 your body makes. This situation is known as hypocapnia. Hypocapnia often happens when people have panic attacks and breathe too quickly. However, it can also point to more serious health issues like sepsis or kidney failure. A common sign of low blood test results is having too much acid in the blood, which can lead to metabolic acidosis. Symptoms of this condition include confusion, tiredness, and trouble breathing.
- Feeling dizzy
- Tingling or weakness in your hands and feet
- Trouble breathing
- A rapid heartbeat
- Chest pain or discomfort
If you feel any of these symptoms, visit a doctor. A doctor can help you understand what is happening and suggest the best way to treat it.
How to Treat Low CO2 in Blood
If your blood test results show unusual CO2 levels, you should talk to your doctor. Together, you can find out why this is happening. Then, you can work on a treatment plan. This plan may include changes to your lifestyle, adjusting your medications, or doing more tests.
Finding the Underlying Cause of Abnormal Results
Your doctor will check to find out why your CO2 levels are not normal. They might look at your medical history and do a physical exam. Your doctor may ask for extra tests too. If you have trouble breathing, they may do lung function tests. If there are problems with your metabolism, they might check your kidney function.
Personalized Treatment Plan
- Treatment is based on the reason CO2 levels are not normal.
- Here are some examples:
- If being overweight causes high CO2 levels, consider joining a weight loss program.
- Breathing exercises can help with anxiety that leads to fast breathing.
- People with chronic lung problems may feel better with oxygen therapy.
- Dialysis is required if kidney failure causes low total CO2 levels.
- Medications that change the balance of electrolytes might need adjustments.
Knowing the signs of too much or too little CO2 is important for your health. When you understand what causes unusual results, you can make a plan that fits your needs. This helps you manage your condition better.
Abnormal CO2 levels in the blood suggest an issue with breathing or how the body works. This could be due to congestive heart failure. When CO2 levels are high, you may feel short of breath, confused, or have muscle cramps. On the other hand, low CO2 levels might make you feel dizzy, numb, or lead to a fast heart rate.
You need to make a plan for CO2 levels and health issues connected to them. Treatment can include lifestyle changes. Breathing exercises can help with anxiety. Oxygen therapy can assist with chronic lung problems. Dialysis may be necessary if low CO2 is due to kidney failure. We might also need to change medicines that impact electrolyte balance.
Summary
CO2 blood tests are key for your health. It's important to understand why CO2 testing matters. You should know what can change test results, signs of too much or too little CO2, and what treatments are available for these problems. This knowledge can help you spot issues early. Early detection can prevent problems from becoming worse.
Don't delay. Start taking care of your health today. Book your CMP test, which has the CO2 blood test, at Discounted Labs. Note that the CMP requires fasting for 12 hours before the test.
CO2 Blood Test Results FAQs
What is a normal CO2 level?
Normal levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) are about 23-29 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). These levels can change a bit based on the lab and the method they use. It is best to talk to a healthcare provider. They can help you understand your carbon dioxide levels and what the results mean for your health.
Is low CO2 acidosis or alkalosis?
Low carbon dioxide levels in the blood are known as respiratory alkalosis. This condition can happen from breathing too fast, or it may result from other health issues. When someone has this, the carbon dioxide levels fall. This change can also upset the body's balance of acids and bases.
How is a low CO2 blood test result diagnosed and treated?
Low carbon dioxide levels in the blood are known as hypocapnia. A blood test can measure the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood. This condition can happen due to hyperventilation, metabolic alkalosis, and several other medical issues.
Treatment for low CO2 levels varies based on the cause. If a person is hyperventilating, fixing their breathing can help raise CO2 levels to normal. If a medical condition causes low CO2, the main goal will be to manage that condition.
Talk to a healthcare provider. They can help you find the right diagnosis. They will also set up a plan for you.
Can I make lifestyle changes to treat low CO2 in the blood?
Low CO2 in the blood can happen because of breathing too fast, health issues, or certain lifestyle choices. If you want to boost your CO2 levels, you can try:
- Breathing exercises can help you.
- Pursed-lip breathing is helpful.
- Diaphragmatic breathing is good too.
- These exercises can help you control your breathing.
- They may also raise CO2 in your blood.
- Reduce stress. Feeling tense or anxious can make you breathe faster and lower your CO2 levels.
- Do things that lower stress, and you'll feel better.
- Try yoga, meditation, or mindfulness exercises to feel good.
- Stay hydrated by drinking enough water. Good hydration is important for healthy breathing. Not drinking enough can hurt your breathing and drop CO2 levels. Drink water every day to stay hydrated.
- Don't push yourself too hard during exercise.
- Intense workouts can make you breathe quickly and drop your CO2.
- Exercise slowly and focus on your breathing techniques.
- If your CO2 levels don't get better, talk to a healthcare provider.
- If you worry about your breathing, reach out to a healthcare provider.
- They can check you and provide options for improving your health.
You can feel better and be healthier by changing your lifestyle. It is also important to see a doctor if your blood has low CO2 levels.
Sources
- Everything you need to know about a CO2 blood test - Medical News Today
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2) in Blood - MedlinePlus
- CO2 Blood Test - Mount Sinai
- CO2 Blood Test: What You Need to Know - Healthline
- Bicarbonate (HCO3) Blood Test Overview - WebMD









