Gynecomastia: Types, Causes, and Treatments
According to the National Institute of Health, gynecomastia can affect more than 50% of adolescent boys during puberty.
At the same time, gynecomastia can also affect up to 65% of men between 27 and 92 years, depending on their lifestyle, habits, drug intake, and other factors.
But what is gynecomastia and why so many men get it? Is it dangerous? And what can you do to treat it effectively and safely?
Keep reading this article to find out everything you need to know about gynecomastia, its types, causes, and treatment options.
Table of Contents
What is Gynecomastia?
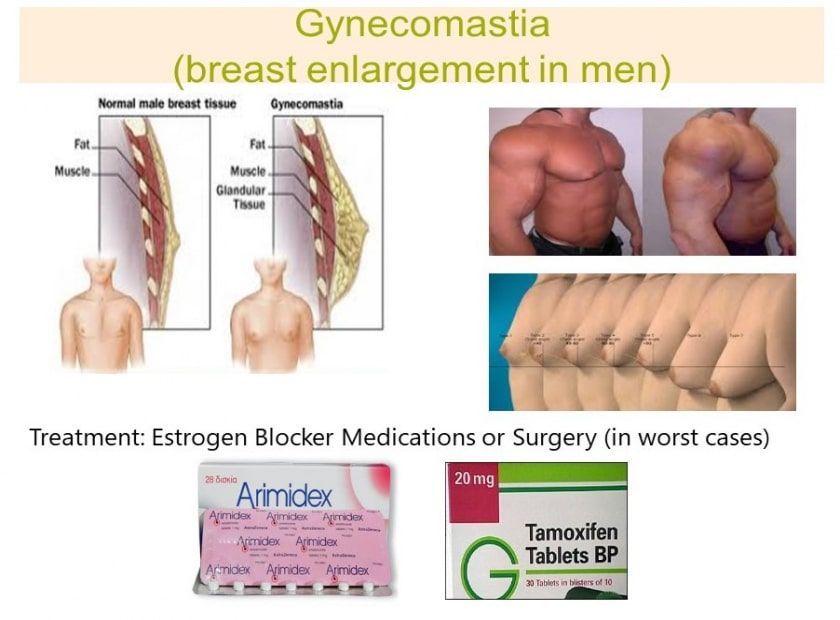
In simplest terms, gynecomastia is commonly known as “man boobs.” It’s a health issue characterized by an increase of the breast tissue in adolescent boys as well as adult males.
Although this type of condition doesn’t usually pose serious health risks, it can have profound psychological consequences. Men simply don’t like having breasts which look like those of women. The prevalence of gynecomastia in seniors over 50 years of age is approximately 70%. In rare cases, untreated gynecomastia can lead to different types of diseases, including breast cancer, so that’s why it’s essential to accurately diagnose and treat them.
Gynecomastia can also be referred to as male breast enlargement, and it splits into three main categories - physiological, pathological, and pharmacological. Let’s take a closer look at each one.
What Kinds of Gynecomastia Are There?
Physiological Gynecomastia
This type of gynecomastia is usually caused by an imbalance in the testosterone and estrogen ratio in the body. As you probably know, these two are the essential sex hormones, and they need to be present in specific quantities in the bloodstream in both males and females.
For example, men have 40 times more testosterone than females, but they also have small amounts of estrogen. This estrogen helps with libido, bone density, and other critical bodily functions. Women have higher quantities of estrogen, but small amounts of testosterone for libido, muscle mass, mood, etc.
Men who have relatively more estrogen than necessary to balance testosterone tend to develop gynecomastia. This can be caused by various factors.
-
Neonatal Gynecomastia
It usually happens at birth when the ratio of estrogen to testosterone is imbalanced. It should resolve itself after a few weeks. Parents must seek a doctor's help if the gynecomastia persists after one year.
-
Pubertal Gynecomastia
This type of gynecomastia usually happens among teenagers who reach puberty. The balance of estrogen to testosterone goes out of whack, and the breasts of adolescent boys grow more than usual. The issue should get resolved automatically in less than two years. If it doesn’t more investigations are required to determine the cause of this type of gynecomastia.
-
Aging Gynecomastia
Adult males who get old will also experience mild gynecomastia, which is caused by advanced age. This process happens as a result of an increase in aromatase activity. In other words, the brain, fat tissue, liver and testicles convert a larger portion of testosterone into estrogen. The resulting higher estrogen to testosterone ratio causes aging gynecomastia.
What Hormone Inbalances Can Cause Gynecomastia?
This type of gynecomastia is usually caused by an increase in estrogen hormones, a decrease in androgen hormones or a combination of both. Here are a few hormone inbalances that can cause gynecomastia:
1. Androgen deficiency
Gynecomastia can be caused by a testosterone deficiency in males of all ages. When testosterone levels drop, estrogens become more prevalent and might dictate a breast enlargement in men.
In such cases, gynecomastia acts as a symptom of testosterone deficiency and it helps individuals become aware of this health issue. Testosterone deficiency is usually associated with a higher aromatization rate (which converts more testosterone to estrogen) and a decrease in the production of luteinizing hormone (LH).
The Klinefelter Syndrome is usually associated with hypogonadism in those patients. Unfortunately, this health issue can increase the likelihood of developing breast cancer; that’s why it’s crucial to test the testosterone levels as soon as possible if gynecomastia is observed in patients.
Breast enlargement caused by androgen deficiency can be treated with testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). In these cases, testosterone is administered in an exogenous manner by using injections, creams, pills, gels, etc.
2. Hyperprolactinemia
Hyperprolactinemia is a health condition in which a male has higher levels of the hormone prolactin in his bloodstream. Prolactin is a hormone present in all mammals which allows them to produce milk.
Hyperprolactinemia might be caused by a type of growth on the pituitary gland, a condition known as a prolactinoma. This growth triggers an increase in the production of prolactin, which causes hyperprolactinemia. Certain medications can cause increased prolactin. One side effect of this condition is gynecomastia.
3. Estrogen Excess
Different types of estrogens cause an increase in breast development in both males and females. However, males tend to have a much smaller amount of estrogen in their bodies, so the breast enlargement stops after a while. In some cases, an excessive amount of estrogen can be produced, which leads to gynecomastia.
Tumors tend to cause excess estrogen production, which in turn leads to gynecomastia. The administration of exogenous estrogens can also trigger gynecomastia in males of all ages. Patients who develop tumors also experience other symptoms such as Cushing's syndrome, weight loss, and an accumulation of fat in the abdominal area.
In some cases, gynecomastia can also be a symptom of more severe disease such as testicular cancer. People who have gynecomastia should also receive a thorough investigation of the testicles to see if more serious health issues are present.
4. Thyroid Problems
The thyroid gland is a vital contributor to the healthy development of a male. Conditions such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism can lead to abnormal secretion of testosterone, decreasing the levels of this hormone in the bloodstream. As a result, estrogens become more prevalent, and they cause gynecomastia in most patients.
If patients are assessed, and their gynecomastia is caused by thyroid issues, receiving thyroid treatment is the most appropriate solution. After the thyroid hormonal balance is restored, gynecomastia usually goes away on its own.
5. Obesity
People who are obese usually have gynecomastia as well. This happens because the aromatization of testosterone into estrogen occurs in the adipose tissue. As a result, having more fat around the body allows more testosterone to be converted into estrogen, which results in breast enlargement.
6. Growth Hormone Excess
Another cause of gynecomastia might be represented by an excessive amount of growth hormone and IGF-1 in the bloodstream. These hormones are responsible for growing muscle mass and bones. Studies show a correlation between gynecomastia in pubertal boys and a high amount of growth hormone and IGF-1 in the blood. Men using growth hormone or growth hormone releasing hormones should be aware of this issue.
7. Other Causes
Gynecomastia might also be caused by different other health conditions. For example, chronic liver disease can significantly decrease testosterone production, which leads to breast enlargement and gynecomastia.
Resuming a healthy diet after a long period of starvation can also cause gynecomastia. That's because, during periods of food scarcity, the production of testosterone is reduced. Testicular damage might also trigger enlargement of breasts in men.
Pharmacological Gynecomastia Caused by Medications
It has been discovered as a result of numerous studies that gynecomastia can also be caused by various drugs. For example, some medications can reduce testosterone production; others might cause an increase in estrogen hormones or disrupt the sensitivity of androgen receptors. Opioids can also cause gynecomastia.
1. Performance-Enhancing Drugs (PEDs) in Athletes
It is a well-known fact that various performance-enhancing drugs are taken by athletes and non-athletes to increase their sports performance. Anabolic-androgenic steroids (AAS) are usually used to increase muscle mass, reduce recovery time, and improve sports performance. One side effect of abusing such drugs is the development of gynecomastia since most anabolic steroids shut down the body’s own testosterone production, which increases the estrogen to testosterone ratio.
Abusing PEDs cause breast enlargement in men because it increases the aromatization process. This converts more testosterone into estrogen and gynecomastia appears as a result. After a prolonged period of abuse, other health complications can arise, such as erectile dysfunction and infertility.
2. Getting Exogenous Estrogen
The estrogen hormone can be absorbed into the bloodstream in various ways and usually accidentally. For example, animals who are treated with estrogen-rich food or drugs are eaten by men who absorb some of these hormones. Similarly, some creams which are used to treat baldness can cause an increase in estrogen production, which leads to gynecomastia.
Similarly, soy-based products tend to contain estrogens (known as phytoestrogens), which can get into the bloodstream. Lavender and tea tree oil also contain phytoestrogens and are commonly found in food and cosmetics.
3. Using Recreational Drugs
Different types of drugs, such as marijuana can also cause gynecomastia if abused. The experts are not yet aware of why this process happens, but there is a health condition known as marijuana-induced gynecomastia. It is believed that this drug can reduce the production of testicular testosterone, which leads to hypogonadism and gynecomastia.
How to Treat Gynecomastia
As you probably have figured it out, there's no one-size-fits-all treatment for gynecomastia in men. This condition can be a problem by itself, or it can be a symptom of a more severe health issue which needs to be investigated immediately.
As a general rule of thumb, gynecomastia can be caused by an increased aromatization of testosterone to estrogen, increased IGF-1, decrease thyroid function with or without a decrease in testosterone production. These two conditions can be triggered by drug abuse, organ damage, genetics, or other factors.
Once the first physical symptoms are observed, the patient needs to visit his healthcare provider immediately to do more investigations. Gynecomastia is characterized by an increase of the hard to the touch breast tissue, especially under the nipple area. Therefore, it shouldn’t be confused with fat mass.
The doctor can perform various investigations such as doing a blood test for testosterone and/or for estrogen levels. Depending on these results, the doctor might recommend other tests to discover why the testosterone to estrogen ratios are unbalanced. If testosterone blood levels are low, doctors prescribe testosterone replacement therapy. If estrogen is high while testosterone is normal, doctors usually prescribe tamoxifen. However, certain more advanced gynecomastia cases require surgery to extract breast gland tissue.
In some cases, gynecomastia is caused by other underlying issues. For example, if it's caused by thyroid problems, the thyroid gland must be treated with appropriate medication. If gynecomastia is caused by liver damage, addressing the liver might help to fix gynecomastia for good.
Those who are obese should consider losing weight to alleviate their gynecomastia symptoms. Entering a weight loss program and eating healthier foods can facilitate the process of losing weight.
Gynecomastia FAQ
Here are a few answers to some of the questions you might have about gynecomastia.
1. Is Gynecomastia Painful?
Some patients might experience mild pain in their chest area as well as tenderness, especially when gynecomastia gets into an advanced state. However, the pain is not sharp or intense, and it usually goes away once proper treatment for gynecomastia is administered.
2. Does the Breast Tissue Subside Once Gynecomastia Is Treated?
One of the main concerns of patients with gynecomastia is whether the breast tissue will continue to "hang" after the condition is treated. Unfortunately, the tissue will not subside on its own in most cases, but there are solutions to this problem. Once the underlying cause of gynecomastia is treated, patients can perform small surgeries to remove the excess breast tissue and achieve a more "manly" chest.
3. Does Scarring Occur After Removing the Breast Tissue?
Luckily, the scarring is minimal around the nipple area and almost invisible. Patients can go to the beach and not worry that someone will see that they had gynecomastia surgery because the scarring is virtually non-existent.
4. Are There Any Other Drugs or Substances Which Cause Gynecomastia?
Certain drugs or substances might cause gynecomastia such as marijuana, steroids, or other performance-enhancing drugs. However, men might develop breast tissue enlargement as a result of consuming high amounts of alcohol too. Alcohol can damage the liver, which in turn decreases the production of testosterone.
At the same time, certain drugs such as spironolactone, ketoconazole, and others can also trigger the development of gynecomastia. Cimetidine, which is a drug used to treat ulcer, is also associated with this type of health issue.
Conclusions
Treating gynecomastia can be done with relative ease these days, as long as you are aware of its existence. For a complete and thorough test which helps you diagnose this condition quickly, check out the Gynecomastia Test Panel. This lab test panel provided by Discounted Labs can be done using a blood sample, and you get the results in just a few business days. The results can help your doctor decide what therapies are best for you to eliminate your gynecomastia.
Reference:
Sansone A, et al. Gynecomastia and hormones. Endocrine. DOI 10.1007/s12020-016-0975-9





